Types of Agents in AI: Examples, Architecture & Working
Artificial Intelligence (AI) isn’t just about algorithms and data — it’s about agents that perceive, think, and act intelligently in their environments. If you’ve ever asked “what are agents in AI?” or “What is agentic AI?” what are wondered how intelligent systems like self-driving cars or chatbots operate, you’re about to find out. In this blog, we’ll explore the types of agents in AI, their architecture, and real-world AI agent examples. We’ll also touch on knowledge-based agents in AI and give a quick guide on how to build AI agents — all explained simply for engineers, students, and aspiring AI professionals.
What is an AI Agent?
An AI agent is a system that perceives its environment through sensors and acts upon it through actuators. It uses logic, data, or learning models to make intelligent decisions — just like humans do when responding to their surroundings.
Think of an AI agent as an “autonomous decision-maker.” From virtual assistants like Siri to trading bots and autonomous drones, AI agents interact with the world to achieve specific goals.
The Architecture of Agents in AI: How They Sense, Reason and Respond
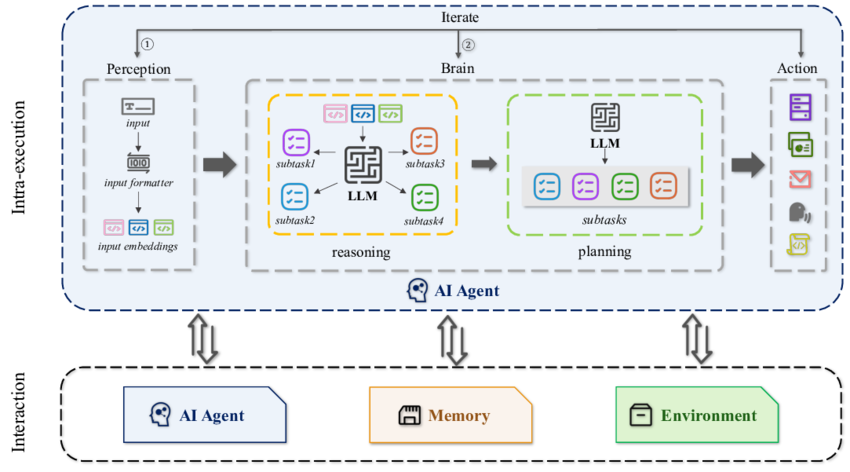
Image Source: Research Gate
The AI agent architecture defines how an agent processes information, makes decisions, and performs actions. It’s the blueprint that connects perception, reasoning, and action.
Most AI agent architectures follow this sequence:
-
Perception – The agent gathers data using sensors (e.g., cameras, microphones, APIs).
-
Reasoning – It processes that information using algorithms or knowledge bases.
-
Decision-making – The agent decides the best action to achieve its goal.
-
Action – Finally, it performs an action via actuators or system responses.
This architecture allows agents to adapt and learn from their environment, leading to agentic AI — systems capable of self-improvement and proactive behavior.
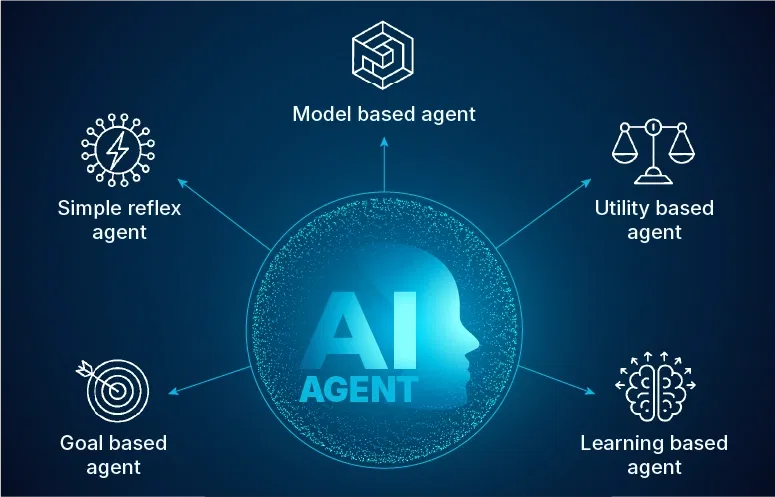
Types of Agents in AI

Image Source: SoftWeb Solutions
AI agents can be classified into several categories depending on how they perceive, decide, and act. Let’s break down the five main types of AI agents with examples and use cases.
1. Simple Reflex Agents in AI
Definition: Simple reflex agents respond directly to current percepts, ignoring history or future outcomes. Their decisions are rule-based, using “if–then” conditions.
Example: A thermostat adjusting temperature based on current readings or a chess bot responding to specific moves.
Use Case: Basic automation systems, reactive robots, and simple AI-driven devices.
2. Model-Based Reflex Agents in AI
Definition: These agents consider both the current input and a model of the world. They understand how their actions affect the environment.
Example: A self-driving car uses sensors and stored maps to navigate obstacles.
Use Case: Autonomous navigation, robotics, and game-playing AI systems.
3. Goal-Based Agents in Ai
Definition: Goal-based agents act to achieve specific objectives. They don’t just react — they plan and reason to reach desired outcomes.
Example: A delivery drone choosing the fastest route to deliver a package.
Use Case: Logistics, strategic gaming AI, and path-planning systems.
4. Utility-Based Agents in AI
Definition: These agents go beyond goals and measure performance using a “utility” function — they seek the best possible outcome among alternatives.
Example: An AI trading bot analyzing multiple stock options to maximize profit.
Use Case: Financial forecasting, recommendation engines, and decision-support systems.
5. Learning Agents in AI
Definition: Learning agents can improve their performance over time by learning from past experiences. They adapt to new situations and refine their decision-making models.
Example: ChatGPT, virtual assistants, and autonomous robots that improve through user feedback.
Use Case: Natural language processing, reinforcement learning systems, adaptive gaming, and robotics.
Knowledge-Based Agents in AI
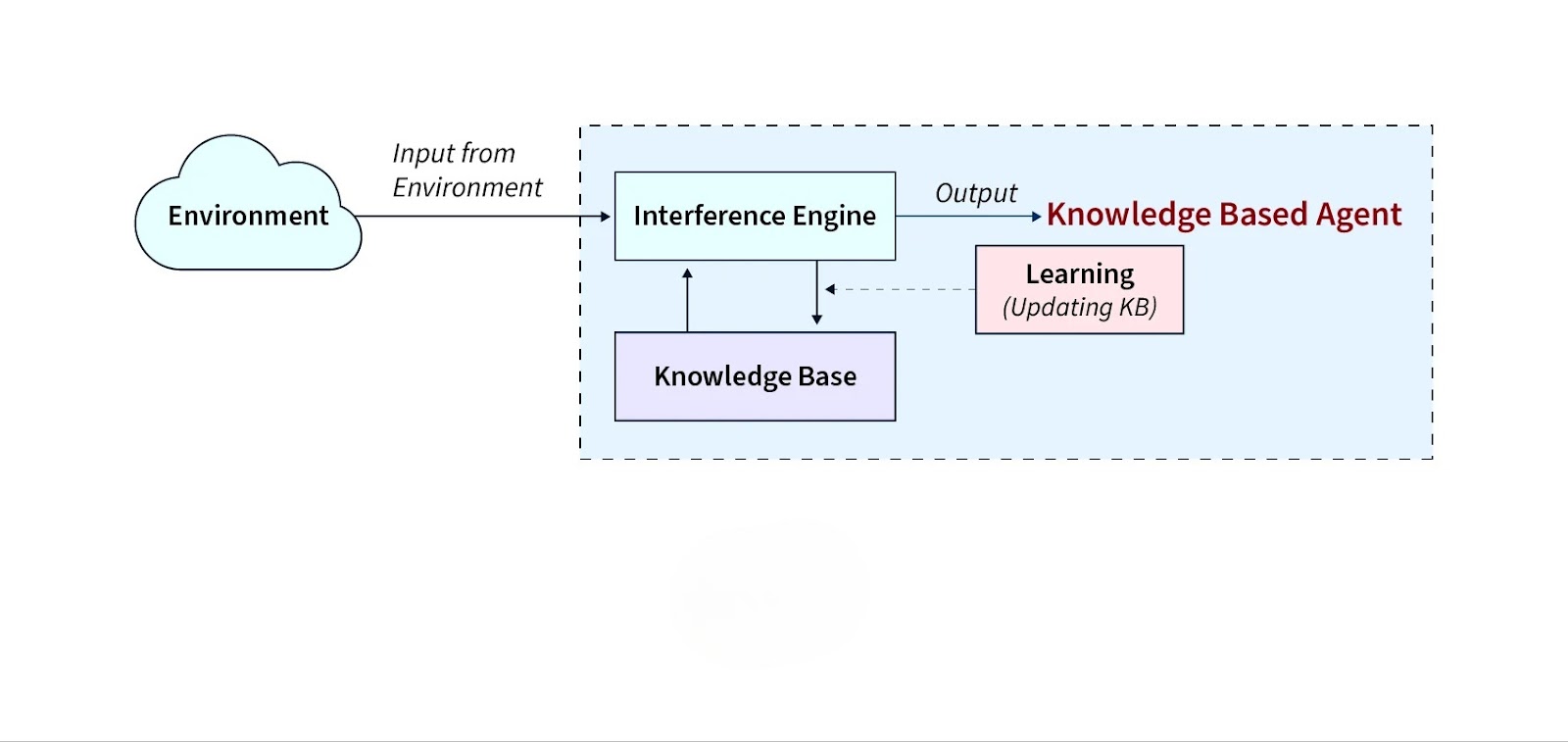
Image Source: Applied AI Course
A knowledge-based agent is a special type of intelligent system that stores facts, rules, and information about the world. It uses this “knowledge base” to reason, infer, and make decisions intelligently.
For example, in medical diagnosis systems, a knowledge-based agent uses stored information about symptoms and diseases to identify possible conditions.
Key Components:
-
Knowledge Base (KB): Contains facts and rules.
-
Inference Engine: Draws conclusions using logical reasoning.
-
Learning Component: Updates the knowledge base with new insights.
This architecture is crucial in expert systems, chatbots, and virtual assistants that require human-like reasoning capabilities.
What Is Agentic AI?
Agentic AI refers to AI systems that not only react but also act with intention and autonomy. These systems can make decisions, initiate actions, and adapt strategies without constant human input.
Unlike traditional AI that follows strict programming, agentic AI learns, reasons, and collaborates — the foundation of next-gen intelligent systems.
Example: AutoGPT or AI research assistants that can plan, search, and execute multi-step tasks independently.
This is where AI is heading — from reactive systems to self-directed intelligent agents.
AI Agents Examples in Real Life

Image Source : EastGate Software
Here are a few AI agent examples you likely encounter daily:
-
Voice Assistants: Alexa, Siri, and Google Assistant — goal-based and learning agents.
-
Autonomous Vehicles: Model-based reflex and learning agents processing sensory data.
-
Recommendation Systems: Netflix and Spotify — utility-based agents optimizing user satisfaction.
-
Trading Bots: Goal and utility-based agents analyzing data to execute profitable trades.
-
Robotic Process Automation (RPA): Simple reflex agents handling repetitive office tasks.
Each of these showcases how different types of AI agents power modern applications — from your smartphone to large-scale enterprise systems.
How to Build AI Agents
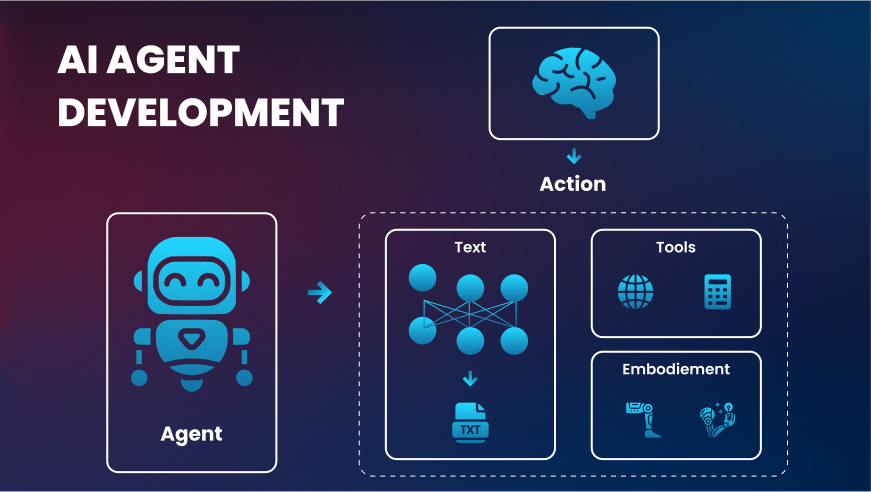
Image Source: Solulab
Creating AI agents involves combining machine learning, data processing, and software engineering. Here’s a simplified roadmap for aspiring developers to build ai agents:
-
Define the Agent’s Purpose: What problem will it solve? (e.g., scheduling, predicting, optimizing).
-
Design the Architecture: Choose between reflex, goal-based, or learning agent models.
-
Implement Perception: Add data inputs (APIs, sensors, or datasets).
-
Add Reasoning and Decision Logic: Use rules, neural networks, or knowledge bases.
-
Train and Test the Agent: Use simulation or real-world data to evaluate performance.
-
Deploy and Monitor: Integrate it with applications and keep improving via feedback.
Learning how to build AI agents opens endless opportunities — from building chatbots to developing complex autonomous systems.
Key Takeaways
-
AI agents are the backbone of intelligent systems — perceiving, reasoning, and acting autonomously.
-
The types of agents in AI include simple reflex, model-based, goal-based, utility-based, and learning agents.
-
Knowledge-based agents use logical reasoning, while agentic AI pushes toward self-governing intelligence.
-
Real-world examples include chatbots, self-driving cars, and recommendation engines.
-
Understanding AI agent architecture helps you design smarter, adaptive systems.
Final Thought
AI is evolving rapidly, and understanding the types of agents in AI is your gateway to building next-generation intelligent solutions. Whether you’re a student or a professional switching careers, mastering AI agents is a powerful step toward becoming future-ready.
So — what type of AI agent will you build next?


